La Niña Coming: From One Climate Extreme to Another
As we’re all aware, weather is never static. Weather conditions and patterns are always changing and are difficult to predict. One very recent example of this is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). ENSO is a cycle of warming and cooling events in the equatorial Pacific Ocean and the atmosphere above it. These periodic events take place over roughly 2-7 year intervals. The resulting variability in oceanic and atmospheric temperatures has a range of effects on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns across the world.
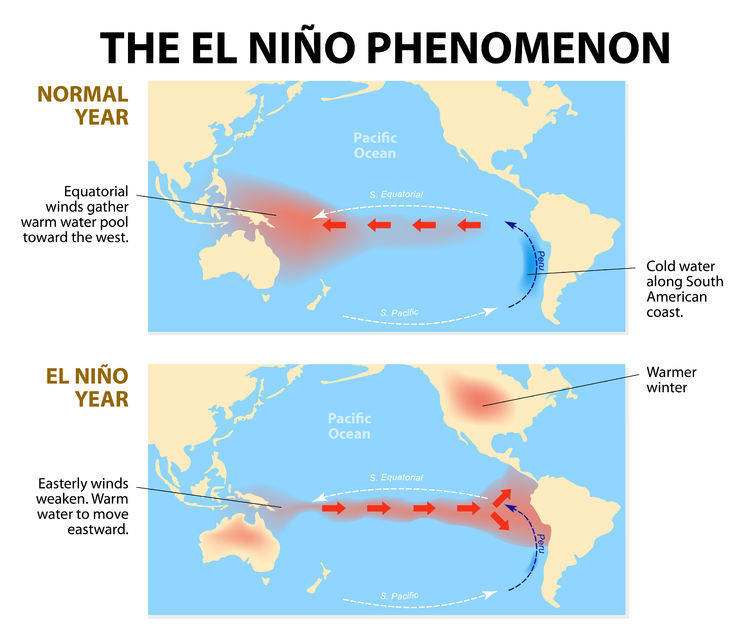
With ENSO, the cycle can shift form its neutral or normal state, to a warm phase – El Niño, or a cool phase – La Niña. We’ve been in one of the strongest El Niño phases on record for the last 2 years. During El Niño, the typical East-to-West winds weaken in the equatorial Pacific, which drives warm waters from the western Pacific to the eastern Pacific. This causes warm ocean surface temperatures and heavy precipitation in northern South America, and dry conditions in Australia and Indonesia.
With the El Niño phase we’re currently in, there have been a lot of extreme weather phenomena. The monsoon rains weakened in India, resulting in food shortages, West Africa has been in a drought, Australia experienced record heat, Brazil experienced excessive rains, and the northern hemisphere winters were warmer than usual. For Texas specifically, there’s been increased precipitation events, making 2015 Texas’ wettest year on record.
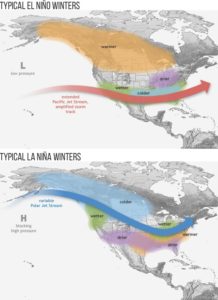 This month though, scientists from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) have issued an official “La Niña Watch.” They predict that El Niño will phase out in late spring or early summer, and will shift to La Niña for the fall and winter. So we can soon expect to see generally opposite conditions than we have been experiencing with El Niño.
This month though, scientists from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) have issued an official “La Niña Watch.” They predict that El Niño will phase out in late spring or early summer, and will shift to La Niña for the fall and winter. So we can soon expect to see generally opposite conditions than we have been experiencing with El Niño.
La Niña results when cool ocean water intensifies the East-to-West winds across the equatorial Pacific Ocean. This causes warm oceanic temperatures in the western Pacific, which means heavy rainfall for Australia and Indonesia. Conversely, it causes cool oceanic temperatures in the eastern Pacific, resulting in dry conditions in South America.
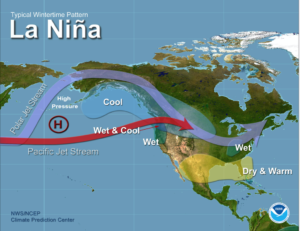 During La Niña winters, the U.S. experiences dry and warm conditions in the southern states, but wet and cool conditions in the Pacific Northwest and northern plains. We can expect there to be a lot of snow in the Pacific Northwest while there’s drought in California and Texas. In previous La Niña periods, the lack of rainfall negatively impacted Texas water supplies and crops. With La Niña, there’s also an increased chance of Atlantic hurricanes since the temperature and moisture flow associated with it creates ideal conditions for hurricane formation.
During La Niña winters, the U.S. experiences dry and warm conditions in the southern states, but wet and cool conditions in the Pacific Northwest and northern plains. We can expect there to be a lot of snow in the Pacific Northwest while there’s drought in California and Texas. In previous La Niña periods, the lack of rainfall negatively impacted Texas water supplies and crops. With La Niña, there’s also an increased chance of Atlantic hurricanes since the temperature and moisture flow associated with it creates ideal conditions for hurricane formation.
Even worse, research indicates that because of global climate change, El Niño and La Niña may hit twice as often as they did before. Climate models indicate that an extreme La Niña may hit every 13 years now instead of every 23 years, and an extreme El Niño may hit every 10 years now instead of every 20 years. Since a warmer atmosphere can hold more water and moisture, rainstorms can increase in intensity. For example, during a future El Niño, the West Coast may experience heavier downpours than usual. During a future La Niña, the added moisture in the air may make northeast snowstorms much stronger.
If the weather is always undergoing different cycles and is constantly changing, then why does an upcoming La Niña matter? Shifts in precipitation and temperature patterns alter crop production abilities, which will impact the prices of goods all over the world. Various commodities will be affected by the upcoming La Niña:
- India: extended monsoon
- Threatens iron ore and onions.
- South Africa: excess rains
- Benefits corn and sugar cane.
- Northern United States: excess rains and colder winters
- Benefits winter wheat, but could increase gas demand.
- Southern United States: dry and warm
- Threatens corn, soybeans, wheat, and cattle.
- Australia: heavy rains
- Threatens coal, wheat, and sugar, but could see restocking of cattle and sheep farms.
- Coral bleaching
- South-East Asia: heavy rains
- Threatens rubber, palm oil, coal, and tin.
- Colombia: heavy rains
- Threatens coffee.
- Argentina and South Brazil: dry
- Threatens soybean and corn yields.